Sandwich Panels in Aerospace - A341
| Sandwich Panels in Aerospace | |
|---|---|
| Perspectives article | |
| |
| Document Type | Article |
| Document Identifier | 341 |
| Themes | |
| Tags | |
| Prerequisites | |
|
Webinar Date
Presenter
Mark Shead
| |
Introduction
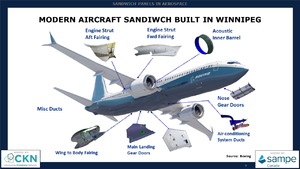
Sandwich structures (sandwich panels) are excellent for applications that benefit from high strength to weight ratios. They find themselves in a variety of applications in aerospace, marine, automotive, wind energy, and other industries. A previous webinar, Introduction to Sandwich Structures - Materials and Processing provided an introduction and overview of sandwich structures.
This webinar provides a more detailed look into sandwich panel use, particularly on commercial airplanes. The presentation focuses on honeycomb core fabrication including cutting, shaping, splicing and potting. Information is also provided on some of the challenges with processing sandwich panels and provides insights into mitigation strategies.
This presentation is part of CKN’s ongoing Application + Impact (AIM) webinar series. Content discussed in the webinar is linked to the Knowledge in Practice Centre, allowing users to access this and other content in a consistent and coherent manner.
Presenter
Mark Shead
Materials and Process Engineer
Associate Technical Fellow
Boeing Canada Winnipeg
Webinar
Webinar slides
Webinar slides available by clicking on the icon below
Additional information for select chapters
| Chapter | Chapter Title | Links to related information in the Knowledge in Practice Centre |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Welcome & introductions | N/A |
| 2 | Knowledge in Practice Centre | |
| 3 | Outline and history | |
| 4 | Honeycomb core | |
| 5 | Core splicing | |
| 6 | Heat forming | |
| 7 | Core shaping | |
| 8 | Potting | |
| 9 | Reticulation | |
| 10 | Challenges: core conforming to skin | |
| 11 | Challenges: pressure impacts of potted locations | |
| 12 | Challenges: core movement | |
| 13 | Q&A | N/A |
Related pages
| Page type | Links |
|---|---|
| Introduction to Composites Articles | |
| Foundational Knowledge Articles | |
| Foundational Knowledge Method Documents | |
| Foundational Knowledge Worked Examples | |
| Systems Knowledge Articles | |
| Systems Knowledge Method Documents | |
| Systems Knowledge Worked Examples | |
| Systems Catalogue Articles | |
| Systems Catalogue Objects – Material | |
| Systems Catalogue Objects – Shape | |
| Systems Catalogue Objects – Tooling and consumables | |
| Systems Catalogue Objects – Equipment | |
| Practice Documents | |
| Case Studies | |
| Perspectives Articles |
| About | Help |
Welcome
Welcome to the CKN Knowledge in Practice Centre (KPC). The KPC is a resource for learning and applying scientific knowledge to the practice of composites manufacturing. As you navigate around the KPC, refer back to the information on this right-hand pane as a resource for understanding the intricacies of composites processing and why the KPC is laid out in the way that it is. The following video explains the KPC approach:
Understanding Composites Processing
The Knowledge in Practice Centre (KPC) is centered around a structured method of thinking about composite material manufacturing. From the top down, the heirarchy consists of:
- The factory
- Factory cells and/or the factory layout
- Process steps (embodied in the factory process flow) consisting of:
The way that the material, shape, tooling & consumables and equipment (abbreviated as MSTE) interact with each other during a process step is critical to the outcome of the manufacturing step, and ultimately critical to the quality of the finished part. The interactions between MSTE during a process step can be numerous and complex, but the Knowledge in Practice Centre aims to make you aware of these interactions, understand how one parameter affects another, and understand how to analyze the problem using a systems based approach. Using this approach, the factory can then be developed with a complete understanding and control of all interactions.
Interrelationship of Function, Shape, Material & Process
Design for manufacturing is critical to ensuring the producibility of a part. Trouble arises when it is considered too late or not at all in the design process. Conversely, process design (controlling the interactions between shape, material, tooling & consumables and equipment to achieve a desired outcome) must always consider the shape and material of the part. Ashby has developed and popularized the approach linking design (function) to the choice of material and shape, which influence the process selected and vice versa, as shown below:
Within the Knowledge in Practice Centre the same methodology is applied but the process is more fully defined by also explicitly calling out the equipment and tooling & consumables. Note that in common usage, a process which consists of many steps can be arbitrarily defined by just one step, e.g. "spray-up". Though convenient, this can be misleading.
Workflows
The KPC's Practice and Case Study volumes consist of three types of workflows:
- Development - Analyzing the interactions between MSTE in the process steps to make decisions on processing parameters and understanding how the process steps and factory cells fit within the factory.
- Troubleshooting - Guiding you to possible causes of processing issues affecting either cost, rate or quality and directing you to the most appropriate development workflow to improve the process
- Optimization - An expansion on the development workflows where a larger number of options are considered to achieve the best mixture of cost, rate & quality for your application.
To use this website, you must agree to our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy.
By clicking "I Accept" below, you confirm that you have read, understood, and accepted our Terms and Conditions and Privacy Policy.





